RADIO FREQUENCY
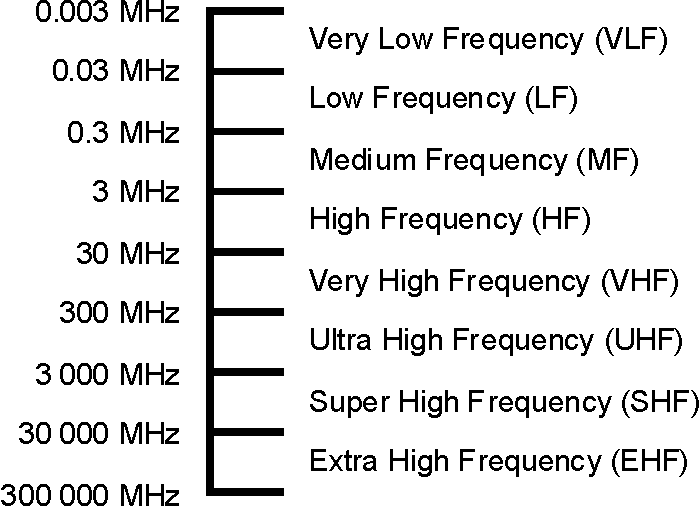
Radio frequency is the activity representing the oscillation rate of electromagnetic radiation spectrum, electromagnetic radio waves, from frequencies starting from 300GHz to as low as 9kHz. Radio frequency is measured in units called hertz, which represent the number of cycles per second when a radio wave is transmitted. One hertz equals one cycle per second. The unit Hertz is named in honor of the 19th-century German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz. With the utilization of antennas and transmitters, an RF field can be used for various types of wireless broadcasting and communications.
When it involves choosing the right radio, the difficult task is to choose the right bandwidth to be utilized. the 2 major wavelengths used for communications are VHF (Very High Frequency) and ultrahigh frequency (Ultra High Frequency).
VHF
VHF’s frequency range is from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. VHF has 10 times longer wavelength. This means the waves are longer with VHF therefore it travels further. The VHF radio band
specifically for commercial radios is between 130 -174 MHz. If you're operating largely outdoors, a VHF radio maybe the most effective selection, particularly if you are employing a base station radio inside and you add the external antenna. The higher you can place the antenna, the further you can transmit and receive.VHF radios also have a smaller number of available frequencies.One benefit of VHF wireless radios is that battery life is almost always better than for similar
UHF units. For handheld radios this is a plus.The VHF band is used for two-way radio communication. a good deal of satellite communication and broadcasting is done at VHF.
VHF waves, not like longer waves, are not strongly reflected from the atmosphere; therefore, they don't bend round the Earth’s curvature and cannot be transmitted beyond the horizon. VHF waves are restricted to use in short-range, line-of-sight communications, together with radio and television broadcasting, and in electronic navigation systems.
UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) refers to the band of electromagnetic radiation with a frequency varying between 300 MHz and 3GHz. This band is also called as the decimetre band, with a wavelength starting from 1 m to 1 dm. UHF is used for data transmission with shorter wavelength and high frequency. Since the size of antenna is directly proportional to the size of the waves, the antennas for UHF are short and stout. Higher the frequency band lower the size of antenna.The broadcast range is shorter than VHF.
UHF is used in two-way navigation, wireless local area network and communications, radio and security systems.
For example, When you’re in an area with lots of small
obstacles, such as a circle track or stadium race where there’s lots of people, you’re going to need a
signal that can travel in between gaps of those obstacles to the receiver you’re talking with. This is
where UHF signal will provide a greater range because of the smaller waves. VHF is suitable for wide range, but in this case UHF is used for better transmission quality.



No comments:
Post a Comment