ANTENNA
As the developed of electronics increased in recent years, scientists and engineers have found a way to eliminate the use of traditional antennas such as Yagi antenna,Rabbit ear antenna etc.But the antennas aren't going anywhere,they are replaced by new technologies.Although antennas are generally considered to be outdated, telecommunication companies are finding ways to innovate the antenna for next generation of electronics. As antennas are smaller, lighter,and more powerful than ever before they are used in wide areas such as 3D printers and manufacturing technique.

An antenna is a transducer that changes over radio frequency (RF) fields into alternating current or the other way around. There are both receiving and transmission antennas for sending or accepting radio transmissions. Antennas assume a significant job in the activity of all radio hardware. They are utilized in remote networks, portable communication and satellite correspondence.
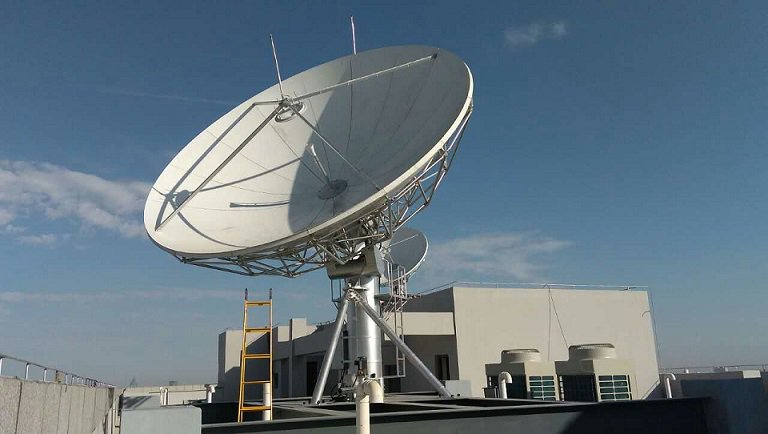

They are arranged with metallic conductors where the electrical connection are given to the receivers and transmitters. Current is passed through these conductors and an alternating magnetic field is created.They induce voltage to the antenna.The magnetic field is coupled with similar oscillating electric field.It allows electromagnetic waves for propagation.
There are several reason for using these antennas but the important reason is to provide a simple way to transfer signals when other methods are impossible.Working of any wireless device requires transmitting and receiving signals(or data) this is only possible with the use of antennas.There are many situation in which cables are preferred over wireless communication with antennas(like high speed Ethernet or the connection between gaming console and the T.V., for example).
As the developed of electronics increased in recent years, scientists and engineers have found a way to eliminate the use of traditional antennas such as Yagi antenna,Rabbit ear antenna etc.But the antennas aren't going anywhere,they are replaced by new technologies.Although antennas are generally considered to be outdated, telecommunication companies are finding ways to innovate the antenna for next generation of electronics. As antennas are smaller, lighter,and more powerful than ever before they are used in wide areas such as 3D printers and manufacturing technique.

An antenna is a transducer that changes over radio frequency (RF) fields into alternating current or the other way around. There are both receiving and transmission antennas for sending or accepting radio transmissions. Antennas assume a significant job in the activity of all radio hardware. They are utilized in remote networks, portable communication and satellite correspondence.

They are arranged with metallic conductors where the electrical connection are given to the receivers and transmitters. Current is passed through these conductors and an alternating magnetic field is created.They induce voltage to the antenna.The magnetic field is coupled with similar oscillating electric field.It allows electromagnetic waves for propagation.
WHY DO WE NEED ANTENNAS?
There are several reason for using these antennas but the important reason is to provide a simple way to transfer signals when other methods are impossible.Working of any wireless device requires transmitting and receiving signals(or data) this is only possible with the use of antennas.There are many situation in which cables are preferred over wireless communication with antennas(like high speed Ethernet or the connection between gaming console and the T.V., for example).
Stay tuned to learn about the types of antennas which will be posted next week.